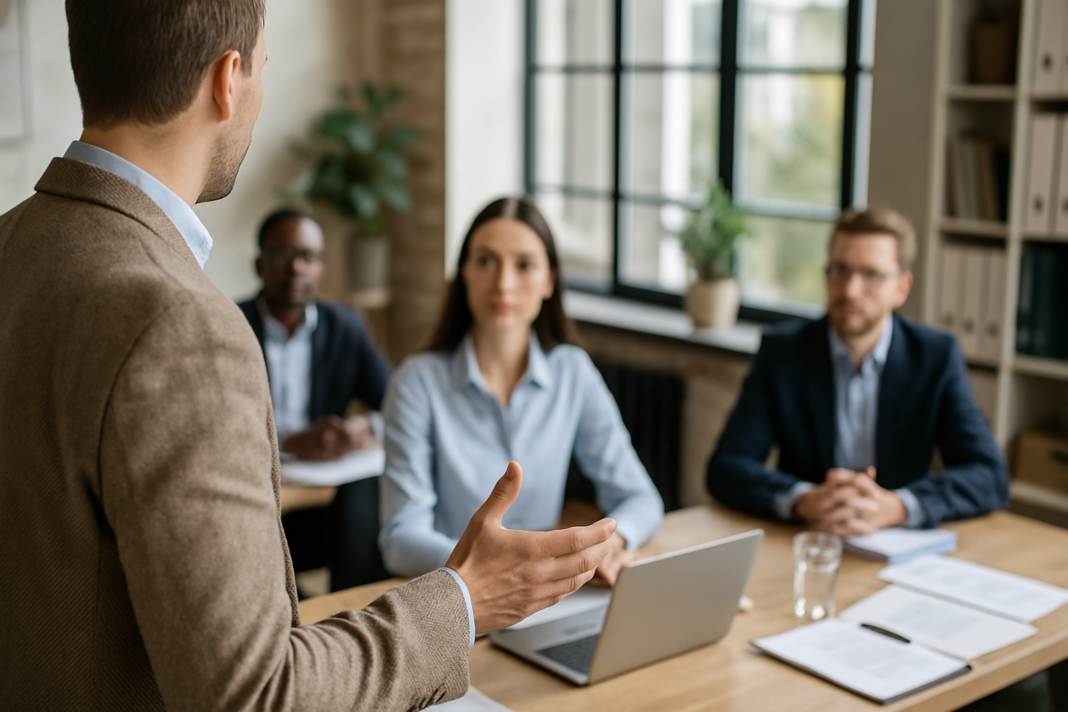
Why leadership expectations define team behavior
Every organization operates according to a set of visible and invisible standards. These standards guide how decisions are made, how work is prioritized, and how people treat responsibility. At the center of these standards are leadership expectations. They influence performance more deeply than rules, policies, or incentives because they shape daily behavior.
Teams do not respond primarily to what leaders say. They respond to what leaders consistently do. Before expecting effort, discipline, accountability, or excellence from others, leaders must establish those qualities through their own actions. When expectations are not modeled, they lose legitimacy. When they are consistently demonstrated, they become part of the organizational culture.
This article explains five essential actions a leader must take before expecting those same behaviors from a team. Each section addresses a foundational principle that determines whether expectations are resisted, ignored, or fully adopted.
Understanding leadership expectations
How expectations influence performance
Leadership expectations function as behavioral signals rather than instructions. They communicate what matters most through repeated actions and decisions. Teams observe how leaders manage pressure, respond to failure, and allocate attention. These observations form the basis for how team members choose to behave.
When expectations are unclear or inconsistent, teams default to minimal compliance. When expectations are clear and reinforced through action, teams develop confidence and autonomy. Performance improves because effort is aligned with purpose rather than guesswork.
The difference between stated and demonstrated expectations
Many leaders articulate high standards verbally but fail to reinforce them behaviorally. This disconnect creates confusion. Teams quickly learn to prioritize demonstrated behavior over spoken values. For expectations to be effective, they must be visible in daily leadership conduct.
1. Create clarity before expecting alignment
Direction as the foundation of leadership expectations
Alignment cannot exist without clarity. Before expecting a team to execute effectively, leaders must define direction in concrete terms. This includes clear objectives, measurable outcomes, and explicit priorities. Ambiguous goals undermine trust and slow execution.
Leadership expectations related to alignment require leaders to eliminate uncertainty. When direction is clear, teams can make independent decisions that support shared goals.
Translating vision into actionable standards
Vision alone is insufficient. Leaders must translate vision into specific standards that guide behavior. This includes defining what success looks like and how progress will be evaluated. Clear standards reduce friction and prevent misalignment across teams.
2. Demonstrate discipline before enforcing standards
Behavioral consistency as a leadership signal
Discipline is one of the most observable leadership traits. Before expecting punctuality, preparation, or focus, leaders must display these behaviors consistently. Teams notice inconsistencies immediately. When leaders disregard standards, enforcement loses credibility.
Leadership expectations related to discipline rely on repetition. Occasional compliance is not enough. Consistency establishes authority without the need for constant supervision.
The cost of selective enforcement
Selective enforcement damages trust. When leaders hold others accountable but excuse themselves, standards collapse. Discipline must be universal. Leaders who apply standards evenly reinforce fairness and predictability, which strengthens team commitment.
3. Accept responsibility before demanding accountability
Ownership as a leadership obligation
Accountability cannot be delegated downward without being demonstrated upward. Before expecting team members to take responsibility for outcomes, leaders must accept responsibility for results. This includes acknowledging mistakes and addressing failures directly.
Leadership expectations around accountability are reinforced when leaders model ownership. This behavior encourages initiative and reduces fear driven decision making.
How responsibility builds trust
When leaders accept responsibility, teams feel protected rather than exposed. This psychological safety enables honest communication and early problem identification. Accountability becomes a shared value instead of a punitive mechanism.
4. Communicate openly before expecting trust
Transparency as a prerequisite for trust
Trust does not emerge from authority. It develops through communication. Before expecting loyalty or engagement, leaders must communicate openly about decisions, constraints, and priorities. Transparency aligns understanding and reduces speculation.
Leadership expectations related to trust require consistent information sharing. Silence creates uncertainty. Uncertainty erodes confidence faster than unfavorable news.
Providing context, not just instructions
Effective communication includes context. When teams understand why decisions are made, they commit more fully to execution. Context transforms compliance into engagement and reinforces shared responsibility.
5. Invest in capability before expecting performance
Development as a leadership responsibility
High performance requires capability. Before expecting results, leaders must ensure teams are equipped with skills, tools, and feedback. Leadership expectations that ignore development lead to exhaustion rather than improvement.
Training, coaching, and structured feedback demonstrate commitment to long term success. These investments signal that performance expectations are realistic and supported.
Linking growth to expectations
When development aligns with standards, improvement becomes measurable. Leaders who support growth create resilient teams capable of adapting to change. Performance increases because individuals feel enabled rather than pressured.
How leadership expectations shape culture
From individual behavior to collective norms
Culture is the accumulation of repeated behaviors reinforced by leadership. Leadership expectations shape what is tolerated and rewarded. Over time, these behaviors become norms that guide action even in the absence of supervision.
Strong cultures reduce reliance on authority. Teams internalize standards and regulate themselves. This autonomy accelerates decision making and strengthens accountability.
The compounding effect of consistency
Consistency compounds over time. Small behaviors, repeated daily, shape long term outcomes. Leaders who maintain alignment between words and actions create durable cultures that sustain performance beyond individual leadership tenures.
Common breakdowns in leadership expectations
Misalignment between intent and action
The most common failure occurs when leaders express expectations they do not follow. Teams interpret this as permission to ignore standards. Credibility declines, and performance follows.
Leadership expectations must be reinforced through visible behavior. Otherwise, they become ineffective.
Excessive or conflicting standards
Too many expectations dilute focus. Leaders must prioritize a limited number of critical behaviors. Clear, focused expectations are easier to adopt and sustain.
Leadership expectations in high performance environments
Why elite teams operate differently
High performance teams function with internalized standards. Leadership behavior establishes expectations that teams enforce collectively. Peer accountability replaces hierarchical control.
In these environments, leaders intervene less frequently. Expectations guide behavior automatically, enabling speed and adaptability.
Sustaining excellence through example
Elite performance is sustained when leaders continue to model standards even after success is achieved. Complacency erodes expectations. Ongoing discipline preserves momentum.
Maintaining leadership expectations over time
Reinforcement through decisions and consequences
Expectations must be reinforced through decisions, rewards, and consequences. Leaders signal priorities through resource allocation and recognition. Inconsistency weakens standards.
Sustained leadership behavior ensures expectations remain relevant and respected.
Self awareness and reflection
Leaders must regularly evaluate whether their actions align with stated standards. Feedback and reflection prevent drift and maintain integrity.
Evaluating the effectiveness of leadership expectations
Behavioral indicators of alignment
Effective expectations manifest as increased ownership, reduced oversight, and faster decision making. Leaders should measure behavior rather than intentions.
Feedback loops help identify gaps early and allow corrective action before issues escalate.
Leadership expectations and strategic insight
Why insight driven leadership expectations outperform intuition
Leadership expectations reach their highest level of effectiveness when they are informed by insight rather than assumption. Many leaders rely on personal experience or instinct to set standards, yet intuition alone is insufficient in complex organizational environments. Insight driven leadership expectations are built on observation, reflection, and pattern recognition across teams, processes, and outcomes.
When leaders ground expectations in insight, they reduce bias and improve fairness. Teams are more likely to accept standards when they are clearly connected to observable realities rather than personal preference. Insight allows leaders to distinguish between performance issues caused by effort and those caused by structural constraints. This distinction is critical before holding teams accountable.
Leadership expectations supported by insight also evolve more effectively. Static standards fail in dynamic environments. Leaders who regularly analyze internal behavior, market conditions, and operational feedback are better positioned to adjust expectations without weakening authority.
Connecting leadership expectations to organizational learning
Organizations that treat leadership expectations as learning instruments outperform those that treat them as fixed rules. Each expectation generates data through behavior. Leaders who pay attention to this data gain insight into capability gaps, communication failures, and cultural misalignment.
This learning oriented approach aligns closely with broader leadership and business insights discussed in professional analysis platforms such as the Startupik insights category at Startupik, where strategic reflection is emphasized as a prerequisite for sustainable growth. Insight transforms leadership expectations from control mechanisms into development tools.
When leaders integrate learning into expectations, teams feel supported rather than monitored. Standards become shared goals instead of imposed constraints. This shift increases engagement and reduces resistance.
Using insight to refine leadership expectations
Refinement requires feedback. Leaders must observe not only outcomes but also the behaviors that produce them. If expectations are not met, the correct response is not immediate enforcement but analysis. Leaders should ask whether expectations were realistic, clearly communicated, and adequately supported.
Insight driven refinement strengthens credibility. Teams recognize when leaders are thoughtful rather than reactive. This recognition increases trust and willingness to adjust behavior. Leadership expectations gain authority because they are perceived as fair and informed.
Refinement also prevents expectation inflation. Leaders often add new standards without removing outdated ones. Insight allows leaders to simplify expectations, focusing on behaviors that deliver the highest impact.
Balancing consistency and adaptation
Consistency is essential, but rigidity is dangerous. Insight enables leaders to maintain consistent principles while adapting execution. Leadership expectations should remain stable in values but flexible in application.
For example, accountability may be constant, while performance metrics evolve. Insight helps leaders preserve core standards while adjusting measurement criteria to reflect changing conditions. This balance maintains trust while supporting progress.
Teams respond positively when leaders explain adjustments transparently. Insight based adaptation reinforces the perception that expectations are designed to help the organization succeed rather than to exert control.
Leadership expectations as strategic signals
Every expectation sends a signal about what matters. Insight allows leaders to evaluate whether these signals align with strategic priorities. If innovation is a priority, expectations must encourage experimentation. If reliability is critical, expectations must emphasize consistency and preparation.
Misaligned signals create confusion. Insight helps leaders detect when expectations contradict stated goals. Correcting these contradictions restores alignment and improves execution quality.
Strategic leaders regularly audit their expectations. They examine which behaviors are rewarded, which are tolerated, and which are discouraged. This audit process ensures leadership expectations remain aligned with long term objectives.
Embedding insight into daily leadership behavior
Insight is not an abstract exercise. It must be embedded into daily leadership behavior. Leaders should reflect on meetings, decisions, and outcomes. Small observations accumulate into meaningful understanding.
This reflective discipline strengthens leadership expectations over time. Leaders become more intentional in how they communicate standards and respond to deviation. Teams experience leadership as deliberate rather than impulsive.
When insight becomes habitual, leadership expectations mature naturally. They become clearer, more consistent, and more credible without requiring constant enforcement.
The long term impact of insight driven leadership expectations
Organizations led by insight driven leaders develop stronger cultures. Expectations are understood, accepted, and reinforced at all levels. Decision making improves because standards are internalized rather than externally imposed.
Over time, this approach reduces dependency on individual leaders. Leadership expectations become embedded in systems, processes, and peer behavior. This institutionalization supports scalability and resilience.
Insight ensures leadership expectations remain relevant as organizations grow and environments change. It transforms expectations from static rules into adaptive frameworks that guide behavior across time and complexity.
Conclusion
Why leadership expectations begin with the leader
Leadership expectations cannot be imposed through authority alone. They must be demonstrated through consistent behavior. Before expecting clarity, discipline, accountability, trust, or performance, leaders must embody these qualities themselves.
When leaders align actions with expectations, standards become culture. Culture sustains performance, builds trust, and enables organizations to grow with stability and purpose.