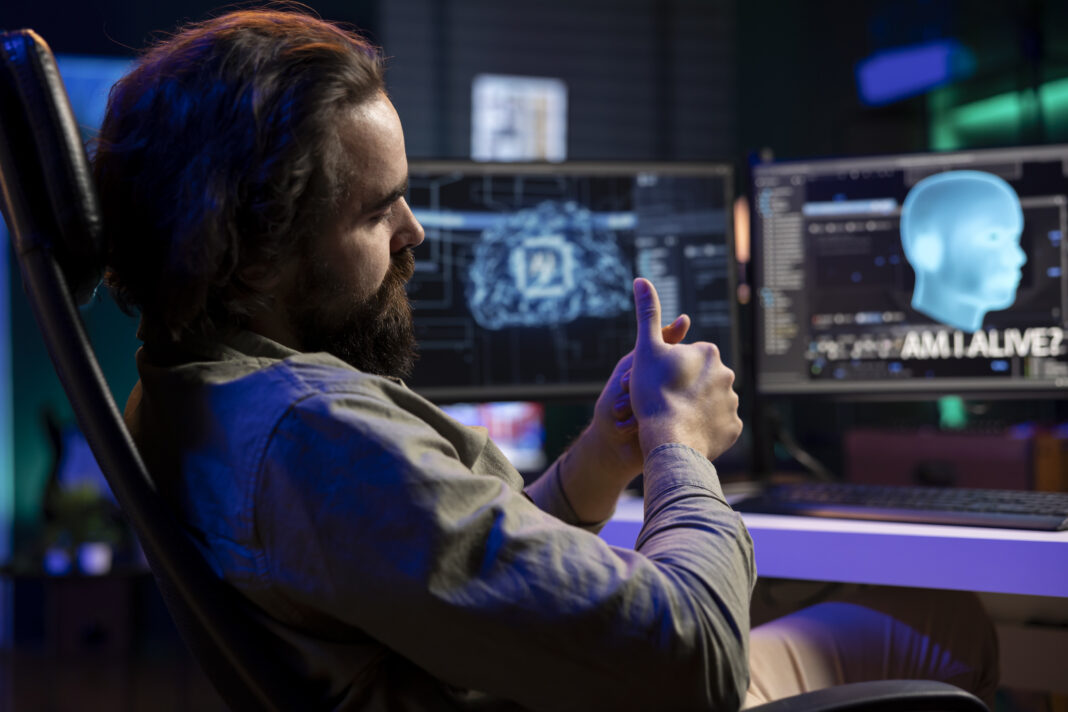
The dark side of AI for startups has become a defining challenge in 2025. Artificial Intelligence is no longer a futuristic buzzword but the engine driving modern entrepreneurship. Startups use AI to accelerate decision-making, improve efficiency, and compete with larger corporations. Yet alongside its promise comes an equally powerful set of risks. The dark side of AI for startups includes hidden dangers in bias, ethics, security, and regulation. Understanding these issues is no longer optional it is essential for survival.
AI has given startups unprecedented tools to scale quickly. From personalized recommendations in e-commerce to chatbots that manage customer interactions, AI allows small teams to achieve large-scale operations. However, this growth also reveals vulnerabilities. The dark side of AI for startups is that the very systems designed to empower innovation can also magnify harm. Startups are often unprepared to handle consequences such as discriminatory outcomes, data breaches, and regulatory fines.
One major concern is algorithmic bias. When startups deploy AI trained on historical data, they risk reinforcing inequality. A recruitment tool, for instance, may unintentionally prioritize applicants from dominant groups while excluding diverse talent. This not only exposes the dark side of AI for startups but also places them at risk of lawsuits and reputational damage. Unlike corporations with large legal teams, startups rarely recover from public scandals that question their fairness.
Another risk is data privacy. AI thrives on collecting and analyzing massive amounts of information. Startups in fintech, healthcare, and education often handle sensitive personal records. If this information is mismanaged, hackers can exploit weaknesses and compromise trust. The dark side of AI for startups emerges most clearly here: one data leak can erase years of hard work. Regulatory penalties under frameworks like GDPR and CCPA only add to the danger, making privacy failures a financial and operational threat.
Regulatory compliance is another hurdle. Governments worldwide are crafting strict rules to control AI deployment. The European Union’s AI Act, for example, categorizes applications based on risk, demanding higher standards for healthcare, finance, and security-related tools. For small companies, navigating these legal landscapes requires time and resources they often lack. The dark side of AI for startups is that a single compliance failure can shut down operations or prevent entry into lucrative markets.
Beyond technical and legal issues, startups must also face ethical dilemmas. Should an AI-powered platform that generates deepfakes for marketing be released without safeguards? What if a healthcare app recommends unsafe treatments because of flawed training data? These scenarios highlight how the dark side of AI for startups is not only about external threats but also about internal responsibility. Entrepreneurs must ask themselves what they should build, not just what they can build.
Job displacement is another part of this equation. Startups frequently automate processes to save costs, but this can eliminate human roles. While efficiency improves, mass adoption of such automation can lead to social inequality and resistance from workers. Here, too, the dark side of AI for startups appears in unexpected ways: public backlash, political opposition, and consumer distrust. Startups aiming to disrupt industries may instead trigger hostility.
The pace of startup culture also adds risk. Moving fast and breaking things might work in app development, but with AI, it can cause widespread harm. Imagine an AI-powered diagnostic tool making false health recommendations or a financial algorithm approving fraudulent loans. These mistakes embody the dark side of AI for startups innovations released too early can damage not only the company but also entire communities.
Dependence on AI also changes startup culture. When founders and teams rely too heavily on algorithms, they risk losing human creativity and empathy. Industries built on trust, like education and healthcare, may suffer from impersonal services that feel mechanical. This reflects another side of the dark side of AI for startups: the erosion of authenticity in fields where human interaction is irreplaceable.
Investors have begun to notice. Funding is no longer directed solely at fast-moving disruptors; investors now ask about compliance, ethical safeguards, and responsible AI design. For startups, this shift means that ignoring the dark side of AI for startups can block investment opportunities. Transparency and accountability are no longer luxuries they are requirements for growth.
On a global scale, inequalities also emerge. Well-funded startups in Silicon Valley or Shenzhen can afford compliance teams, bias audits, and advanced safeguards. Smaller startups, especially in developing regions, cannot compete. This deepens the gap between global players and limits innovation diversity. The dark side of AI for startups is not only about individual companies but about ecosystems that favor the rich and well-resourced.
Despite these challenges, startups cannot afford to reject AI entirely. The technology has become a foundation for competitiveness across industries. The key lies in responsible adoption. Recognizing the dark side of AI for startups is the first step toward managing its impact. By integrating risk assessment, ethical reflection, and compliance planning into their strategies, startups can turn potential threats into opportunities for differentiation.
This article will explore fifteen critical areas where startups encounter these challenges. Organized under the themes of risks, ethics, and regulation, it will outline practical steps and lessons learned from real-world cases. By understanding the dark side of AI for startups, entrepreneurs can create stronger, more resilient ventures. The aim is not to stifle innovation but to encourage responsibility because in 2025, long-term success depends on more than speed. It depends on trust, accountability, and foresight.
Data Privacy and Security Risks
Vulnerability to Data Breaches
The dark side of AI for startups often reveals itself through weak data protection. Startups collect vast amounts of personal and financial information, but they do not always have the infrastructure of larger companies. This makes them an attractive target for hackers. A single breach can expose thousands of customers, ruin reputations, and bring severe financial losses. For many young companies, recovery is nearly impossible after such an event.
Compliance with Data Protection Laws
Global data regulations such as GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California set strict requirements on how startups collect, store, and process information. Failing to meet these obligations can lead to heavy fines. The dark side of AI for startups here is the added cost of compliance. Hiring legal experts, conducting audits, and creating secure systems require resources that startups may not have, yet ignoring them risks shutting down the business altogether.
Misuse of Sensitive Information
AI systems may unintentionally misuse data. For example, predictive algorithms in health startups might draw insights from medical histories without clear patient consent. This can spark legal disputes and public outrage. The dark side of AI for startups becomes clear when innovation crosses ethical lines, even unintentionally. Customers who feel betrayed rarely return, and negative press can end investor interest quickly.
Limited Resources for Security Infrastructure
Large corporations can invest in strong cybersecurity systems, while startups often rely on minimal solutions. This imbalance exposes smaller firms to greater risks. The dark side of AI for startups is not only about external attacks but also about internal weaknesses. Inadequate safeguards, lack of encryption, or poor employee training all increase the chances of costly incidents.
Algorithmic Bias and Fairness
Reinforcement of Social Inequalities
AI systems trained on biased datasets can reinforce discrimination. A hiring platform might favor male candidates over female ones because of historical patterns in resumes. The dark side of AI for startups lies in releasing products that unintentionally create unfair outcomes. For businesses trying to build trust, being labeled discriminatory can be fatal.
Reputational Damage
Bias is not just a technical flaw but a public issue. If customers or advocacy groups highlight unfair AI outcomes, startups may face boycotts or lawsuits. The dark side of AI for startups is that one viral news story can undo years of effort. Unlike established corporations, they often lack the resources to manage crises at scale.
Legal and Financial Consequences
As governments become more aware of algorithmic bias, laws are being drafted to punish companies that fail to prevent it. Fines, investigations, and mandatory audits create financial burdens. The dark side of AI for startups is the reality that innovation can quickly turn into liability when oversight is absent.
Loss of Investor Confidence
Investors increasingly ask about fairness and accountability before funding startups. If a company cannot demonstrate that its AI is free from harmful bias, funding rounds may collapse. This again shows the dark side of AI for startups: ethical negligence does not just affect users, it also shuts down growth opportunities.
Ethical Dilemmas in AI Adoption
Balancing Innovation with Responsibility
Startups thrive on speed, but speed often conflicts with responsibility. AI products released too quickly may harm users. The dark side of AI for startups appears when leaders prioritize growth over ethics, leading to harmful or exploitative outcomes. Responsible scaling is harder but necessary.
At the same time, startups must remember that AI also brings transformative opportunities when used responsibly. For instance, practical strategies in AI marketing for startups show how innovation can drive growth without sacrificing ethical responsibility.
Manipulation and Misinformation
AI tools can be misused to manipulate behavior, spread fake news, or generate deepfakes. A startup developing such technology may intend positive use cases, but once released, it can be weaponized. The dark side of AI for startups here is the lack of control over how products are used in the real world.
Replacement of Human Interaction
Overreliance on AI risks reducing authentic human contact. A mental health app that uses chatbots instead of trained therapists may save costs but fail to provide genuine support. This reflects another side of the dark side of AI for startups, where the pursuit of efficiency erodes empathy and trust.
Investor Pressure vs. Ethical Responsibility
Many startups face investor pressure to monetize quickly, which can lead to ethical shortcuts. Launching a product without proper testing may attract short-term revenue but create long-term harm. The dark side of AI for startups lies in these compromises, which often end up costing more than they save.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Global Variations in AI Law
Different regions have different approaches to AI regulation. The European Union enforces strict standards, the United States prefers sector-based guidelines, and China takes a more centralized approach. For startups, the dark side of AI for startups is the complexity of building systems that comply across multiple markets.
High Compliance Costs
Adapting to diverse legal frameworks demands legal teams, audits, and constant monitoring. This is expensive and time-consuming. The dark side of AI for startups is that compliance costs can consume limited budgets that were intended for innovation.
Risk of Market Exclusion
Failure to comply with AI laws can result in being banned from entire regions. Startups relying on global users may suddenly lose access to crucial markets. This makes the dark side of AI for startups not only legal but also strategic, as access to customers directly impacts survival.
Rapidly Changing Rules
AI regulation evolves quickly, and what is legal today may not be tomorrow. Startups must adapt constantly, which is difficult with limited resources. The dark side of AI for startups lies in the unpredictability of compliance, which creates uncertainty for planning and growth.
Security Threats from AI Misuse
Adversarial Attacks
Hackers can manipulate AI systems to produce false results. For example, altering a few pixels in an image can mislead recognition software. The dark side of AI for startups is that such vulnerabilities can damage credibility and create dangerous scenarios in sensitive industries.
Weaponization of AI Tools
AI systems built for positive purposes can be misused for malicious ones. A text generation model could be repurposed to create phishing emails or extremist propaganda. Startups releasing such tools without safeguards may find themselves associated with criminal activity, showcasing the dark side of AI for startups.
Internal Misuse by Employees
Not all threats come from outside. Employees may exploit AI tools for personal gain or misconduct. Weak oversight and lack of governance increase these risks. The dark side of AI for startups is the internal exposure that can destroy trust within organizations.
Customer Distrust After Security Failures
Even one security incident can cause permanent reputational damage. Customers who feel unsafe will switch to competitors. The dark side of AI for startups is that they cannot afford to lose user trust, as rebuilding it is far more costly than protecting it from the start.
Impact on Employment and Workforce
Automation of Routine Jobs
One of the most visible effects of AI adoption is job automation. Startups often embrace automation to stay lean and reduce costs. Customer support, logistics, and administrative tasks are increasingly handled by AI. While this creates efficiency, the dark side of AI for startups is the social backlash that follows. Workers and unions may resist, seeing automation as a direct threat to livelihoods.
Skill Gaps and Workforce Displacement
AI adoption demands technical skills that many employees do not possess. Startups may unintentionally widen inequality by creating opportunities only for highly skilled talent. The dark side of AI for startups emerges here: they risk alienating large sections of the workforce and reinforcing social divides.
Dependence on AI Instead of Human Creativity
Startups thrive on innovation and creative problem-solving, but overreliance on AI may reduce originality. When companies let algorithms dictate decision-making, they risk losing their unique human edge. This reflects another dimension of the dark side of AI for startups, where efficiency replaces imagination.
Reputational and Social Responsibility Pressure
Companies that displace jobs face not only economic criticism but also reputational harm. Stakeholders now expect startups to show responsibility in how they deploy AI. Ignoring these expectations amplifies the dark side of AI for startups, turning cost savings into long-term image damage.
Dependence on Third-Party AI Systems
Vendor Lock-In
Many startups cannot afford to build proprietary AI and rely on external providers such as cloud platforms and APIs. This dependence creates vendor lock-in. The dark side of AI for startups here is the lack of independence. If the provider changes pricing, restricts access, or shifts policy, the startup may collapse.
Data Ownership Concerns
When startups use third-party AI, data often flows outside their direct control. Questions arise about who owns the training data and resulting insights. The dark side of AI for startups is the risk of losing ownership over their most valuable asset: customer data.
Lack of Transparency in Algorithms
Third-party AI systems rarely reveal their full inner workings. Startups using them may not fully understand how decisions are made. This lack of transparency exposes the dark side of AI for startups, especially when customers demand explanations for critical outcomes.
Hidden Compliance Risks
By depending on external systems, startups may unknowingly inherit legal liabilities. If a third-party provider violates regulations, the startup can still face penalties. The dark side of AI for startups is that responsibility cannot be outsourced, even if the technology is.
Market Manipulation and Unintended Consequences
Exploitative Algorithms
AI systems designed to optimize profits can unintentionally exploit users. For example, pricing algorithms may charge higher fees to vulnerable customers. The dark side of AI for startups emerges when profit-driven tools cross ethical boundaries.
Spread of Harmful Content
AI-driven platforms sometimes amplify misinformation, offensive speech, or harmful trends. A startup creating recommendation systems may find itself criticized for enabling toxicity. This is another case where the dark side of AI for startups undermines brand integrity.
Unpredictable User Behavior
AI models may react in unexpected ways to new data or user behavior. Startups risk losing control over their systems, leading to outcomes they never intended. The dark side of AI for startups is unpredictability, which makes scaling risky.
Risk of Over-Optimization
Focusing too heavily on AI-driven metrics can cause startups to lose sight of broader goals. For example, optimizing engagement might encourage addictive or harmful behaviors. The dark side of AI for startups here is the trap of short-term success at the expense of long-term trust.
Investor Expectations and Pressures
Demand for Rapid Scaling
Investors often push startups to scale quickly, but AI deployment at speed can magnify risks. Releasing untested technology may win short-term revenue but damage credibility. The dark side of AI for startups is that pressure to grow can compromise responsibility.
Ethical Due Diligence by Investors
Venture capital firms now evaluate not just profit potential but also ethical safeguards. Startups that cannot prove responsible AI adoption may lose funding. This again shows how the dark side of AI for startups intersects directly with financial survival.
Short-Term Profit Focus
Investors may prioritize quick returns rather than long-term responsibility. Startups facing this pressure may ignore ethical concerns, only to face backlash later. The dark side of AI for startups lies in these trade-offs that undermine sustainable growth.
Risk of Investor Withdrawal
If scandals arise from biased algorithms, security failures, or regulatory breaches, investors may abandon the startup. The dark side of AI for startups is that funding can disappear overnight, leaving companies stranded.
Global Competition and Unequal Access
Advantages for Wealthy Ecosystems
Startups in developed economies benefit from access to capital, advanced research, and supportive regulation. By contrast, startups in emerging markets face barriers. The dark side of AI for startups is that innovation becomes concentrated in a few global hubs.
Resource Gaps Between Startups
Even within the same country, large, well-funded startups can implement compliance teams and ethical audits, while smaller ones cannot. This creates an uneven playing field. The dark side of AI for startups is that survival often depends more on funding than on innovation.
Regulatory Favoritism
Some governments favor established tech giants over new entrants. This leaves startups disadvantaged and vulnerable. The dark side of AI for startups here is the unfair competition built into regulatory systems.
Long-Term Market Consolidation
If smaller startups fail to manage risks, the industry may consolidate into the hands of a few dominant firms. This reduces diversity and slows innovation. The dark side of AI for startups is that the ecosystem itself becomes less dynamic and more controlled.
Long-Term Unpredictability of AI
Unforeseen Consequences of Rapid Deployment
Startups often race to launch AI-driven products before competitors. Yet the dark side of AI for startups is that rapid deployment can create unforeseen consequences. An AI system trained for one purpose may behave unexpectedly when scaled, leading to harmful results. For example, a recommendation algorithm designed for entertainment might inadvertently spread misinformation.
Difficulty of Testing at Scale
Small startups rarely have the ability to test AI models at the same scale they will operate in the market. Once released, flaws may appear only after thousands of users interact with the system. The dark side of AI for startups is the gap between lab testing and real-world performance.
Ethical Blind Spots
In the rush to innovate, startups often overlook ethical blind spots. Issues such as user manipulation or hidden bias may only emerge later, when damage has already occurred. The dark side of AI for startups is that mistakes are often irreversible, particularly when they affect vulnerable communities.
Risk of Public Backlash
When AI-driven harm becomes visible, public opinion can turn against startups quickly. Unlike established corporations with crisis management resources, startups may collapse under the weight of negative press. The dark side of AI for startups lies in the fragility of their public image.
Cultural and Human Implications
Loss of Human-Centered Design
AI-driven solutions sometimes prioritize efficiency over human experience. In education, healthcare, or mental health, this can reduce empathy and authenticity. The dark side of AI for startups is the replacement of meaningful human interactions with mechanical systems.
Ethical Branding Challenges
Startups that use AI irresponsibly risk being seen as unethical brands. Modern consumers are increasingly concerned about transparency and fairness. If a startup is linked to bias or surveillance, the dark side of AI for startups appears in the form of reputational loss that no marketing campaign can repair.
Shift in Entrepreneurial Values
Startup culture has historically emphasized creativity and disruption. Overreliance on AI may shift this culture toward conformity, as algorithms drive decisions instead of human vision. The dark side of AI for startups here is the erosion of originality in the name of optimization.
Psychological Effects on Users
AI-driven platforms may encourage addictive behavior, reduce attention spans, or increase social anxiety. A startup that unintentionally fuels such outcomes risks long-term criticism. The dark side of AI for startups lies in the unintended psychological harm inflicted on customers.
Governance and Accountability
Lack of Clear Responsibility
When AI systems fail, startups often struggle to determine accountability. Was the error in the data, the algorithm, or the deployment? The dark side of AI for startups is the legal and ethical confusion over responsibility, which can lead to lawsuits and lost trust.
Inadequate Oversight Mechanisms
Many startups operate with minimal oversight structures. Without formal auditing, bias detection, or risk assessment, AI systems may cause damage before issues are discovered. The dark side of AI for startups is the absence of governance frameworks that protect both users and businesses.
Pressure to Self-Regulate
Governments increasingly expect companies to self-regulate while formal laws catch up. For startups, this adds another burden. The dark side of AI for startups is that they must create internal governance systems with limited resources.
Accountability to Stakeholders
Startups must answer not only to customers but also to investors, employees, and regulators. Each stakeholder demands responsibility. The dark side of AI for startups is that failing one group often leads to broader collapse.
Building Responsible AI in Startups
Embedding Ethics from the Start
Responsible AI requires early integration of ethics into design and decision-making. Startups that delay this process face higher risks later. Addressing the dark side of AI for startups means embedding responsibility from day one.
Collaboration with Regulators
Engaging regulators early can help startups navigate complex rules and avoid penalties. Rather than waiting for enforcement, proactive dialogue reduces uncertainty. This turns the dark side of AI for startups into an opportunity for credibility.
Investment in Transparency and Explainability
Users and investors increasingly demand AI systems that can be explained. Transparent systems earn more trust, while opaque ones invite suspicion. Reducing the dark side of AI for startups requires prioritizing explainability in all applications.
Building Trust Through Certification
New standards and certifications for ethical AI are emerging. Startups that adopt these practices demonstrate reliability. This helps counter the dark side of AI for startups by turning compliance into a competitive advantage.
Global Policy and Regulation
The European Union’s AI Act
The EU AI Act sets strict requirements based on risk categories. For startups, high-risk systems face costly obligations such as documentation and monitoring. The dark side of AI for startups is that these rules, while necessary, may exclude smaller firms unable to comply.
The United States’ Sector-Based Approach
The US uses a sector-specific framework, focusing on healthcare, finance, and defense. Startups face fragmented rules that vary by industry. This creates complexity, showing another side of the dark side of AI for startups: navigating inconsistent regulations.
China’s Centralized Oversight
China has implemented strong oversight to ensure AI aligns with state goals. While this accelerates adoption, it limits creative freedom for startups. The dark side of AI for startups in this environment is reduced autonomy.
Push for International Standards
Global organizations are pushing for universal AI standards. For startups, this may simplify compliance in the future. But until then, the dark side of AI for startups is operating in a fragmented, unpredictable environment.
Conclusion
The dark side of AI for startups in 2025 is a reality that no entrepreneur can ignore. While AI provides unmatched opportunities for growth, it also introduces risks that can destroy young companies if left unchecked. Bias, data breaches, regulatory fines, investor withdrawal, and reputational harm are only some of the dangers that arise when AI is deployed without responsibility.
Startups are uniquely vulnerable because they lack the financial and structural resilience of established corporations. A single ethical scandal or compliance failure can end a venture overnight. This fragility makes it critical for startups to recognize the dark side of AI for startups early and prepare strategies to manage it.
The path forward requires a balance of innovation and responsibility. Embedding ethics into product design, investing in transparency, and building strong governance frameworks are no longer optional. They are essential elements of survival. Startups that embrace responsible AI not only protect themselves from risk but also gain competitive advantage by earning trust from customers, regulators, and investors.
Global competition and regulation will continue to evolve, making the environment even more challenging. Startups that succeed will be those that treat the dark side of AI for startups not as a barrier but as a guide. By confronting risks head-on, they can create sustainable businesses that shape the future of technology without sacrificing integrity.
In the end, the story of AI for startups is not only about growth and disruption but about accountability and trust. The dark side of AI for startups is real, but with foresight and responsibility, it can be managed. Startups that rise to this challenge will not just survive the AI revolution they will lead it.