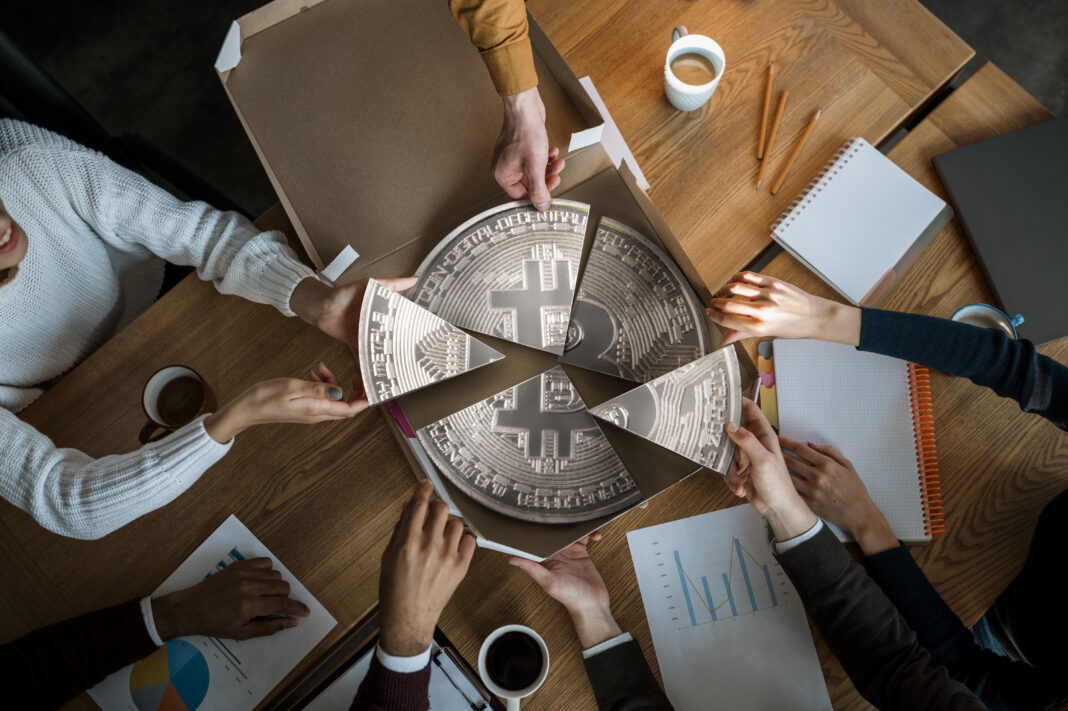
The Promise of Tokenization of Equity
In recent years, startups have been at the forefront of financial innovation, constantly searching for more efficient and inclusive ways to raise capital. Traditional fundraising models such as venture capital, angel investment, and public offerings have long supported entrepreneurial growth, but they often come with limitations. Access is restricted to certain investor groups, processes are costly and time-consuming, and liquidity remains scarce for early backers. Against this backdrop, the tokenization of equity has emerged as a transformative approach.
Tokenization of equity refers to the process of converting ownership shares of a company into digital tokens that exist on a blockchain. These tokens represent actual equity in a startup, but unlike paper-based or centralized records, they are stored and transferred on decentralized networks. This technological shift offers startups a more efficient fundraising mechanism while providing investors with transparent, tradable, and fractional access to early-stage opportunities.
The significance of this model lies not only in technological novelty but in its practical impact. Tokenization of equity democratizes investment, reduces barriers for global investors, and enables startups to scale with greater flexibility. As blockchain adoption continues to expand, tokenized equity is becoming a mainstream option for innovative companies worldwide.
Traditional Fundraising Challenges for Startups
The conventional fundraising ecosystem has long favored well-connected founders and large investors. Startups typically depend on venture capital or angel networks, which can be highly competitive and concentrated in certain regions. Entrepreneurs outside major hubs like Silicon Valley or London often find it difficult to secure sufficient funding, regardless of the quality of their ideas.
Another challenge is the cost of raising funds. Legal, accounting, and administrative expenses related to issuing shares or conducting public offerings can be overwhelming for early-stage ventures. Beyond cost, the process itself is slow and bureaucratic, often taking months to complete.
Liquidity is another major obstacle. Once shares are issued, early investors usually have to wait years until a company is acquired or goes public to exit their investment. This lack of liquidity discourages many potential investors from participating. Tokenization of equity addresses these issues directly by providing faster settlement, fractional ownership, and the possibility of secondary trading in digital markets.
Defining Tokenized Equity in Practice
At its core, tokenized equity is a digital representation of ownership rights. Each token corresponds to a specific portion of a company’s shares, recorded securely on a blockchain. Unlike cryptocurrencies that may serve as payment or utility tokens, equity tokens represent tangible ownership in a business.
The use of blockchain ensures that records are immutable, transparent, and accessible to authorized participants. Investors can verify their ownership instantly without relying on centralized intermediaries. Smart contracts embedded in the tokens can enforce rights such as dividends, voting power, or transfer restrictions.
Tokenization of equity is not about replacing traditional equity but about modernizing how it is issued, recorded, and traded. By combining legal frameworks with digital technology, startups can provide investors with the same rights they would have under conventional shareholding, but with added efficiency and liquidity.
The Immediate Benefits of Tokenization for Startups
The appeal of tokenization of equity for startups lies in tangible benefits that extend beyond hype. First, it broadens access to global capital. Instead of relying on local investors, startups can reach contributors from different regions without being bound by geography.
Second, the cost of issuance is significantly lower compared to traditional fundraising methods. Blockchain-based issuance reduces paperwork, streamlines compliance, and automates processes such as shareholder registration. This allows startups to allocate more resources toward innovation and growth rather than administrative overhead.
Third, tokenization enhances transparency. Every transaction is recorded on the blockchain, ensuring that ownership records are accurate and easily auditable. This level of trust can attract cautious investors who value clarity.
Finally, tokenization of equity improves liquidity. Through secondary trading platforms, investors can sell their tokens before a startup exits, creating a dynamic ecosystem where capital is constantly moving. This liquidity potential makes startup investing more attractive to a broader audience.
Fractional Ownership and Democratization
One of the most revolutionary aspects of tokenization of equity is the introduction of fractional ownership. Traditionally, investing in startups required substantial capital, limiting participation to wealthy individuals and institutional funds. With tokenization, ownership can be divided into much smaller units, allowing retail investors to participate with modest contributions.
Fractional ownership breaks down barriers to entry and creates a more inclusive investment landscape. It also diversifies the investor base, reducing reliance on a small group of backers. This inclusivity benefits startups by spreading risk across a wider pool of stakeholders while simultaneously building stronger community engagement.
For example, a startup raising funds through tokenized equity can invite supporters, customers, and even early adopters to become shareholders with small investments. This not only secures capital but also strengthens brand loyalty. Tokenization of equity therefore plays a dual role: financing growth while fostering community-driven ecosystems.
Blockchain as the Infrastructure of Trust
The success of tokenized equity depends on the reliability of blockchain infrastructure. Distributed ledgers provide the foundation for secure, transparent, and efficient equity management. Transactions cannot be altered retroactively, which reduces fraud and builds investor confidence.
Smart contracts play a crucial role in automating compliance. They can be programmed to enforce legal requirements, distribute dividends, or limit transfers to accredited investors in certain jurisdictions. By embedding rules directly into code, startups ensure that processes run smoothly without constant manual oversight.
Furthermore, blockchain provides global interoperability. Startups that issue equity tokens on recognized platforms can access international investors without complex cross-border procedures. This global reach is a defining feature of tokenization of equity and a key reason why it is gaining traction among entrepreneurs and investors alike.
Tokenization Versus Traditional Fundraising Models
Comparing tokenization of equity with traditional models highlights its disruptive potential. Venture capital provides mentorship and networks, but access is limited and terms often favor investors over founders. Public offerings open access to broader markets but involve massive regulatory costs and are unsuitable for most early-stage ventures.
Equity crowdfunding has tried to democratize fundraising, but it often lacks liquidity and can be restricted to local jurisdictions. Tokenization combines the inclusivity of crowdfunding with the efficiency and transparency of blockchain, while also adding the potential for secondary market trading.
This hybrid nature makes tokenization of equity particularly compelling. It retains the legitimacy of traditional equity while addressing the inefficiencies that have long frustrated both startups and investors. For founders seeking capital and flexibility, it represents a new path forward.
The Regulatory Dimension of Tokenized Equity
Despite its advantages, tokenization of equity exists within a complex regulatory environment. Equity tokens are generally classified as securities, meaning they fall under strict legal frameworks. Compliance with securities laws, investor accreditation, and disclosure requirements remain essential.
Regulatory clarity varies across jurisdictions. Some countries have embraced tokenization with specific guidelines, while others maintain uncertainty or impose restrictions. Startups must navigate this landscape carefully, ensuring that their tokenized equity offerings align with local and international standards.
Adopting robust compliance practices is not just a legal necessity but also a competitive advantage. Investors are more likely to participate in offerings that demonstrate regulatory discipline. Tokenization of equity, when executed responsibly, provides startups with credibility and long-term sustainability in the global market.
Expanding Investor Access through Tokenization of Equity
Traditional investment models have long excluded smaller investors from participating in early-stage opportunities. High minimum investments, geographic limitations, and complex processes often restricted access to wealthy individuals and institutions. Tokenization of equity changes this equation. By digitizing shares into blockchain-based tokens, startups can allow global participation at any scale.
For investors, this means they can buy a fraction of equity tokens and become stakeholders in a startup they believe in. For startups, it opens the door to larger pools of capital from diverse geographies. Tokenization of equity therefore plays a democratizing role, creating opportunities for both sides. This inclusivity also enhances brand loyalty, as customers who invest in a company through equity tokens often become long-term advocates of the product or service.
Lowering Fundraising Costs and Administrative Burden
Raising capital through traditional equity issuance involves significant legal, accounting, and administrative expenses. From drafting documents to registering shares, the process is time-intensive and expensive. Tokenization of equity streamlines this by automating many functions through blockchain.
Smart contracts reduce paperwork by embedding compliance rules directly into digital tokens. Investor records update automatically on the blockchain, eliminating the need for manual registries. Settlement occurs in near real time, reducing delays and errors. The result is that startups can allocate more capital to growth activities rather than administrative tasks.
In addition, tokenized offerings reduce dependence on intermediaries. Instead of relying on multiple layers of brokers, registrars, and custodians, blockchain acts as a unified ledger. Tokenization of equity therefore cuts costs while providing faster and more transparent results.
Transparency and Trust in Tokenized Systems
Trust has always been essential in finance. Investors want to be sure their ownership is secure and properly recorded. Tokenization of equity enhances trust by offering immutable records on a distributed ledger. Every transfer of ownership is logged transparently, leaving no room for manipulation.
This level of accountability is particularly attractive for startups, which often struggle to convince investors of their reliability. With blockchain, startups can provide investors with verifiable proof of ownership and transaction history at any time. Auditors and regulators can also access records more efficiently, reducing friction in oversight.
The transparency of tokenization of equity not only reassures investors but also builds long-term credibility for startups. By committing to open, verifiable systems, companies signal integrity and professionalism in their fundraising practices.
Improving Liquidity with Secondary Markets
One of the greatest innovations brought by tokenization of equity is the potential for liquidity. In traditional systems, startup investors usually wait years until an acquisition or public offering to realize returns. Tokenized equity changes this by enabling trading on secondary markets.
These markets allow investors to buy and sell equity tokens, providing exits long before a startup achieves a major event. For startups, this liquidity attracts a wider range of investors, including those who prefer shorter time horizons. For employees and early supporters, tokenized equity offers an opportunity to realize value earlier than before.
The presence of secondary markets also helps startups refine their valuations. Market-driven pricing reflects real-time demand and investor sentiment, creating a dynamic feedback loop. Tokenization of equity therefore enhances both capital efficiency and market intelligence for young companies.
Legal Considerations in Tokenized Fundraising
While the benefits are compelling, startups must navigate complex legal frameworks. Because equity tokens represent securities, they fall under securities laws in most jurisdictions. Tokenization of equity does not bypass regulation; it requires compliance with the same standards as traditional share offerings.
This includes conducting due diligence, verifying investor eligibility, and adhering to disclosure obligations. Many jurisdictions require strict KYC and AML procedures to prevent misuse. Startups that fail to comply risk fines, reputational damage, or invalidation of their offerings.
To mitigate risks, startups should partner with legal experts familiar with digital securities. Choosing platforms that operate under regulated frameworks provides additional assurance. By aligning innovation with compliance, tokenization of equity becomes a sustainable fundraising strategy rather than a legal liability.
Risks and Challenges in Tokenization of Equity
Like any emerging innovation, tokenization of equity comes with risks. Market volatility can affect investor confidence, especially if secondary trading platforms lack sufficient liquidity. Technical vulnerabilities, such as smart contract bugs or cyberattacks, can create financial losses.
Adoption remains another challenge. Many traditional investors are cautious about blockchain-based assets, preferring established methods of investing. Convincing these stakeholders requires education, transparency, and proven success stories.
Regulatory uncertainty also persists in many regions. Without clear guidance, startups may hesitate to adopt tokenized equity, fearing compliance issues. To overcome these barriers, the ecosystem needs greater collaboration between startups, regulators, and technology providers. Despite these challenges, the long-term potential of tokenization of equity outweighs short-term obstacles.
Launching a Tokenized Equity Offering
For startups considering this path, preparation is crucial. The first step is to evaluate whether tokenization aligns with strategic goals. Startups should analyze their capital needs, investor profiles, and long-term vision before committing.
Next, startups must select the appropriate blockchain platform. Security, scalability, and regulatory compatibility are critical factors. Partnering with experienced token issuance platforms can simplify technical and legal requirements. These platforms often provide turnkey solutions for smart contract deployment, investor onboarding, and compliance management.
Marketing is the final piece. Communicating the benefits of tokenization of equity to potential investors requires clear messaging. Startups must highlight transparency, liquidity, and inclusivity while addressing risks openly. A well-structured campaign builds trust and ensures successful fundraising outcomes.
The Investor Perspective on Equity Tokenization
From an investor standpoint, tokenization of equity introduces both opportunities and responsibilities. The ability to purchase fractional shares expands access to early-stage investments, while liquidity provides more flexible exit options. Transparent records and automated compliance enhance trust in the system.
However, investors must also consider risks. Market volatility, technical vulnerabilities, and evolving regulations can affect returns. Responsible investors should conduct due diligence, assess the credibility of token issuance platforms, and diversify their portfolios.
Overall, tokenization of equity offers a more dynamic and inclusive investment landscape. For those willing to adapt, it represents a significant advancement in how startup investing is conducted.
Secondary Markets as a Catalyst for Tokenization of Equity
Liquidity has always been one of the most pressing challenges in startup investment. Traditional equity models require investors to wait until an acquisition or IPO before realizing returns. This long horizon discourages many potential backers, particularly smaller investors. Tokenization of equity introduces secondary markets where tokens can be traded peer-to-peer or on regulated exchanges, creating liquidity options far earlier in a company’s lifecycle.
These secondary markets allow investors to enter and exit positions based on their own strategies, reducing reliance on rare liquidity events. For startups, this increased investor flexibility can attract a wider range of participants, as capital is no longer tied up indefinitely. By aligning investment timelines with market demand, tokenization of equity reshapes how both startups and investors think about value creation.
Benefits for Early Employees and Supporters
Early employees and loyal supporters often receive shares as part of their compensation or reward structures. In conventional setups, these shares are illiquid for years, offering little practical value until a major corporate event. Tokenization of equity changes this by making employee-owned tokens tradable under certain conditions.
This liquidity provides employees with more immediate financial benefits and strengthens long-term commitment. For startups, offering tokenized equity as part of compensation packages can be a powerful recruitment tool, especially in competitive industries. Early supporters who invest small amounts also gain confidence knowing they can exit through secondary markets if needed.
By expanding benefits beyond founders and large investors, tokenization of equity creates a more inclusive ecosystem that rewards all contributors to startup growth.
Transparency in Valuation Through Market Dynamics
Valuation has traditionally been a closed process dominated by venture capitalists and private negotiations. Tokenization of equity introduces real-time market-driven pricing through secondary trading. As tokens change hands, prices reflect investor sentiment, demand, and company performance.
This transparency allows startups to benchmark their valuation continuously rather than relying solely on periodic funding rounds. It also reduces information asymmetry between founders and investors. While volatility may be higher in early stages, the open feedback loop encourages startups to remain accountable and responsive to stakeholders.
Ultimately, tokenization of equity aligns startup valuations with actual market activity, providing clarity that benefits both companies and investors.
Global Trends in Tokenized Equity Adoption
The momentum behind tokenization of equity is growing worldwide. In Europe, several jurisdictions have embraced digital securities with supportive regulatory frameworks. In Asia, fintech hubs are experimenting with tokenized fundraising to attract international investors. The United States is gradually clarifying its stance, particularly around securities compliance and investor protections.
These regional efforts highlight the global nature of tokenization. Startups are no longer limited by geography when raising funds. Instead, they can issue equity tokens accessible to investors across continents, provided compliance is managed effectively.
This trend also reflects a broader shift toward digital assets in finance. Tokenization of equity is part of a larger movement that includes tokenized bonds, real estate, and commodities. Startups adopting this model are therefore aligning with long-term industry trends that point toward a more digitized financial ecosystem.
Best Practices for Designing Equity Tokens
Successful implementation of tokenization of equity requires careful planning. Tokens must be structured to comply with securities regulations while meeting investor expectations. Startups should focus on four key principles when designing equity tokens:
-
Compliance: Ensure tokens are legally recognized as equity and fulfill all disclosure requirements.
-
Transparency: Provide investors with clear information on rights, governance, and transfer conditions.
-
Security: Use audited smart contracts and secure blockchain networks to protect investor assets.
-
Liquidity: Design tokens with features that facilitate secondary trading while respecting legal restrictions.
By following these principles, startups create equity tokens that inspire trust and deliver value. The tokenization of equity succeeds only when legal, technical, and financial aspects are integrated seamlessly.
Building Investor Trust in Tokenized Fundraising
Trust is central to any investment, and tokenization of equity must address investor concerns proactively. Startups should maintain open communication, providing detailed documentation and regular updates. Demonstrating compliance with securities laws builds confidence that the offering is legitimate.
In addition, startups should partner with reputable issuance platforms and custodians to ensure security. Transparent reporting on token distribution, shareholder rights, and governance structures reassures investors. Over time, consistent performance and communication establish credibility that encourages repeat participation.
Trust also extends to education. Many investors are new to tokenized assets and need clear explanations of benefits and risks. By providing resources and guidance, startups can reduce uncertainty and make tokenization of equity accessible to a broader audience.
The Role of Institutional Investors
While retail investors benefit from fractional ownership, institutional investors are also showing interest in tokenized equity. Hedge funds, venture capital firms, and family offices see potential in the liquidity and transparency offered by blockchain-based securities.
For institutions, tokenization of equity provides opportunities to diversify portfolios and manage risk more efficiently. Secondary markets allow them to adjust positions without waiting years for liquidity events. Moreover, blockchain’s transparent records support more accurate auditing and risk assessment.
As institutional participation increases, tokenized equity will gain further legitimacy and attract more startups to adopt the model. The convergence of retail and institutional interest signals a tipping point in startup fundraising.
Integrating Tokenization into Global Startup Ecosystems
The adoption of tokenization of equity is not happening in isolation. It is becoming a core part of global startup ecosystems, supported by accelerators, incubators, and fintech hubs. These ecosystems provide startups with guidance, mentorship, and tools to navigate legal and technical challenges.
Partnerships between startups and blockchain service providers are critical. Token issuance platforms, compliance firms, and secondary market operators form the infrastructure that makes tokenization viable. Collaboration ensures that startups can focus on innovation while experts handle specialized requirements.
By embedding tokenization into broader ecosystems, startups gain not only capital but also the knowledge and networks needed for sustainable growth. Tokenization of equity is thus both a financial innovation and a community-driven transformation.
Preparing for the Future of Tokenized Fundraising
The trajectory of tokenization of equity suggests continued expansion. As regulations mature and technology evolves, more startups will embrace this model as a standard fundraising option. Future developments may include integration with central bank digital currencies, more advanced secondary markets, and cross-chain interoperability.
Startups that adopt tokenization early gain a competitive advantage. They attract global investors, reduce costs, and provide liquidity options that traditional models cannot match. As the ecosystem matures, tokenization of equity will likely become not just an alternative but the preferred method of startup fundraising.
Case Studies of Tokenization of Equity in Action
Several pioneering startups have already embraced tokenization of equity to raise capital and expand globally. A European fintech issued equity tokens to attract investors across borders, bypassing traditional banking delays. By doing so, it secured funding faster while giving investors fractional ownership and the ability to trade tokens on secondary platforms.
In Asia, a technology startup used tokenized equity to build a community-driven fundraising campaign. Supporters who were already customers invested small amounts and became tokenized shareholders. This strategy not only raised capital but also reinforced customer loyalty.
In North America, a blockchain-focused firm used tokenization of equity to combine traditional venture investment with tokenized shares. The hybrid approach allowed institutional investors to participate while opening smaller allocations to retail backers. These examples show that tokenization of equity is not theoretical but a practical fundraising tool already transforming markets.
How Traditional Finance Is Reacting
Traditional financial institutions initially viewed tokenization of equity with skepticism. Concerns about regulation, security, and market volatility made many cautious. However, as the model matures, banks, exchanges, and investment firms are exploring partnerships with blockchain platforms.
Some exchanges are considering listing regulated equity tokens alongside conventional securities. Custodians are developing digital asset services to manage tokenized portfolios. Venture funds are exploring hybrid models that combine conventional equity with tokenized offerings.
This evolution shows that tokenization of equity is not replacing traditional finance but reshaping it. As institutions adapt, startups gain more pathways to raise funds and investors gain more confidence in the legitimacy of tokenized securities.
The Role of Regulation in Future Adoption
Regulation remains the deciding factor in how fast tokenization of equity spreads. Countries with clear digital securities laws are attracting more startups and investors. Jurisdictions with uncertainty or restrictive rules are slowing adoption.
Global collaboration is likely to accelerate. Regulators are exploring standardized frameworks that align across regions, making it easier for startups to issue equity tokens worldwide. This harmonization would reduce complexity, improve compliance, and create larger investor networks.
For startups, staying proactive about compliance is essential. Adopting strong KYC and AML procedures, transparent reporting, and legal partnerships ensures that tokenization of equity remains sustainable. Regulation, rather than being an obstacle, can ultimately strengthen trust in tokenized fundraising.
Long-Term Strategic Impact for Startups
Adopting tokenization of equity is more than a tactical fundraising choice. It is a long-term strategic move that positions startups for a digital-first financial future. The benefits extend beyond immediate capital to include stronger investor relationships, community engagement, and global scalability.
By lowering barriers to entry, tokenization attracts a wider pool of backers, from retail investors to institutions. By offering liquidity, it creates dynamic markets that keep capital moving. By embedding transparency and compliance, it builds trust and legitimacy.
Startups that embrace tokenization of equity are better equipped to compete globally, adapt to regulatory changes, and align with the digital transformation of finance. The long-term impact is not just more efficient fundraising but a complete redefinition of how startups grow and scale.
Frequently Asked Questions on Tokenization of Equity
What does tokenization of equity mean for startups?
It means converting company shares into blockchain-based tokens that represent ownership. For startups, tokenization of equity provides access to global investors, lower fundraising costs, and potential liquidity through secondary markets.
How is tokenized equity different from traditional shares?
Traditional shares are recorded in centralized registries and often involve complex transfer processes. Tokenization of equity records ownership on blockchain, allowing faster settlement, fractional ownership, and transparent tracking. The rights of shareholders remain similar but are managed more efficiently.
Can retail investors participate in tokenized equity offerings?
Yes, one of the main benefits of tokenization of equity is that it enables fractional ownership. This lowers barriers to entry, allowing retail investors to participate in startup fundraising with smaller contributions than traditional models require.
What risks should startups and investors be aware of?
The main risks include regulatory uncertainty, market volatility, and technical vulnerabilities in smart contracts or exchanges. Both startups and investors must prioritize compliance, security, and due diligence when engaging with tokenized equity.
How do secondary markets improve tokenized fundraising?
Secondary markets provide liquidity, allowing investors to buy and sell equity tokens after issuance. This flexibility reduces reliance on rare exit events like IPOs and acquisitions. Tokenization of equity becomes more attractive because investors have clearer paths to exit strategies.
Are equity tokens legally recognized?
In most jurisdictions, equity tokens are classified as securities and must comply with existing securities laws. Recognition depends on regional regulations, but legal frameworks are steadily evolving to accommodate tokenization of equity.
What is the outlook for tokenization of equity in the next decade?
The outlook is strong. As regulatory clarity improves, technology advances, and adoption increases, tokenization of equity is expected to become a mainstream fundraising model. Startups that adopt early gain competitive advantages in global capital markets.
Conclusion: A New Era in Startup Fundraising
The tokenization of equity is more than a technological experiment. It represents a fundamental rethinking of how startups raise funds, engage investors, and manage ownership. By addressing long-standing challenges such as high costs, limited access, and illiquidity, tokenization provides a compelling alternative to traditional models.
The benefits are clear: global investor participation, fractional ownership, faster settlement, transparency, and liquidity. The challenges, while real, are manageable through compliance, education, and security best practices. As ecosystems mature and regulations align, tokenization of equity is poised to shift from niche adoption to mainstream use.
Startups that embrace this model early will enjoy significant advantages. They will access broader capital pools, attract diverse investors, and scale internationally with greater agility. Investors will benefit from more inclusive opportunities and improved liquidity.
The era of tokenization of equity marks the beginning of a more open, efficient, and democratic financial system. It empowers startups to grow beyond borders and invites investors of all sizes to participate in shaping the future of innovation. This is not just an evolution in fundraising—it is the foundation of a new global startup economy.
The Role of Supportive Ecosystems
Technology alone cannot transform fundraising. The role of supportive ecosystems will remain vital in helping startups navigate uncertainty and apply tokenization effectively. Platforms like Startupik illustrate how guidance, mentorship, and community can bridge the gap between innovation and application.
While blockchain and equity tokenization provide the technical tools, ecosystems ensure that founders know how to use them strategically. By connecting entrepreneurs with investors, legal experts, and peers, Startupik and similar platforms amplify the effectiveness of tokenization of equity. They provide not just access to capital, but also the confidence and knowledge required to manage compliance, build trust, and scale globally.
In this way, tokenization of equity supported by strong ecosystems represents the future of startup fundraising one where innovation, regulation, and collaboration combine to unlock new opportunities for growth.